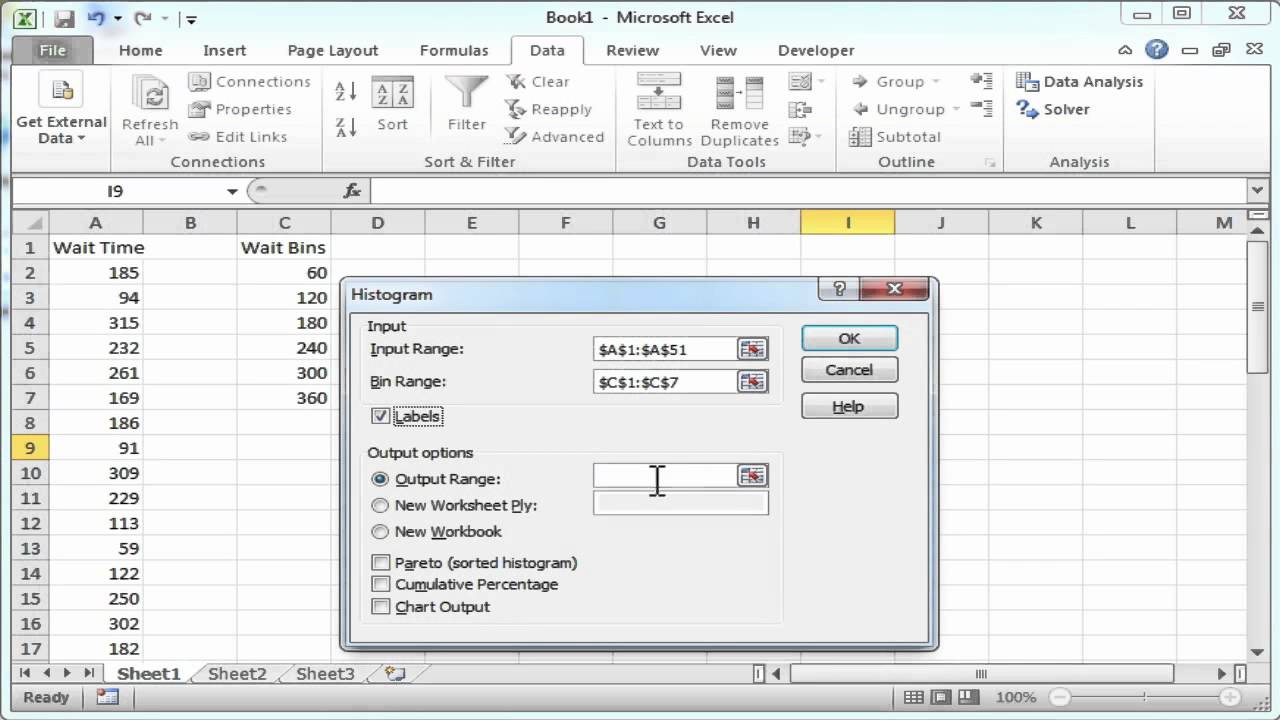
The button will open the Data Analysis dialog, which offers access to a variety of analysis tools. Quick Analysis is a similar set of tools available in Excel 2013. See Microsoft documentation for more information. It applies to Excel 2013 and Excel 2016. Click the Data tab in the main Excel interface, and the Data Analysis button can be found in the Analyze section of the menu. You choose one of these tools, and then a new window will open that asks you to enter configurations specific to the chosen tool.
- Quick Analysis Button Excel 2010
- Where Is Quick Analysis Tool In Excel On Mac Air
- Where Is Quick Analysis Tool In Excel On Mac
Microsoft’s spreadsheet program, Excel, is one of the most useful tools that any manager’s disposal. This dynamic tool can be employed in a multitude of ways, from tracking time, to finances and even sales. One of Excel’s most useful functions is the ability to develop graphs and charts from information which can then be easily analyzed. If you use Excel 2013, you have Quick Analysis – a powerful feature that allows you to quickly analyze data.
Below is an overview of the Quick Analysis tool in Microsoft Excel 2013.
What is Quick Analysis?
In older versions of Excel, if you wanted to visually analyze your data, you would have to first create a chart or graph and then format it. This could take some time and also lead to mistakes, not to mention the fact that it can be a challenge to pick the correct type of chart or graph for your data type.
To make it easier to visualize your data, the Quick Analysis tool was introduced with Excel 2013. This feature allows users to instantly create charts and graphs with the click of a button. It even suggests a visualization method that best fits your data, making picking the correct way to show the information far easier. You can even add miniature graphs to single cells – called Sparklines – that allow you to quickly spot trends without having to look at a full graph.
How to use Quick Analysis
Enter your data in a spreadsheet, and if need be include column headings.
- Select the data you would like to visualize.
- Press Ctrl + Q to open the Quick Analysis gallery. You can also select this by hovering your mouse over the bottom-right corner of the selected cells and clicking the icon that pops up.
- Select the tab you want e.g., Charts for suggested charts. Note: The options available to you will change based on the type of data you have selected.
- Hover your mouse over an option to see a preview of the selected visualization.
- Click on your choice to create the visualization in a new worksheet.
Which Quick Analysis is best?
When you open the Quick Analysis gallery you will notice that you have five different options:
- Formatting – Lets you adjust the data you have highlighted. You can set a color for the data to set it apart and quickly see both high and low values, or even remove formatting altogether.
- Charts – Lets you select different charts and graphs based on the data you have selected. This can include pie charts, bar graphs, line charts, etc. If you press More Charts you will be able to select from a larger list.
- Totals – Lets you calculate numbers in rows or columns. Some useful options include Running Total which keeps a total even when you add more data, and Sum which will total either a column, row or the total sheet. Be sure to pay attention to the colored dots in the icon as they indicate whether a row or column will be calculated.
- Tables – Allows you to create tables or sub-tables using just the selected data. You can also create a pivot table. You should also be able to select More if the type of table you need isn’t there.
- Sparklines – Allows you to add small charts beside your data. These one to two cell visualizations are great for quickly identifying trends within your data.
If you are looking to learn more about Excel 2013 and how you can leverage it in your business, contact us today.
Totals | Tables | Formatting | Charts | Sparklines
Quick Analysis Button Excel 2010
Use the Quick Analysis tool in Excel to quickly analyze your data. Quickly calculate totals, quickly insert tables, quickly apply conditional formatting and more.
Totals
Instead of displaying a total row at the end of an Excel table, use the Quick Analysis tool to quickly calculate totals.
1. Select a range of cells and click the Quick Analysis button.
2. For example, click Totals and click Sum to sum the numbers in each column.
Result:
3. Select the range A1:D7 and add a column with a running total.
Note: total rows are colored blue and total columns are colored yellow-orange.
Tables
Use tables in Excel to sort, filter and summarize data. A pivot table in Excel allows you to extract the significance from a large, detailed data set.
1. Select a range of cells and click the Quick Analysis button.


2. To quickly insert a table, click Tables and click Table.
Note: visit our page about Tables to learn more about this topic.
3. Download the Excel file (right side of this page) and open the second sheet.
4. Click any single cell inside the data set.
5. Press CTRL + q. This shortcut selects the entire data set and opens the Quick Analysis tool.
6. To quickly insert a pivot table, click Tables and click one of the pivot table examples.
Note: pivot tables are one of Excel's most powerful features. Visit our page about Pivot Tables to learn more about this topic.
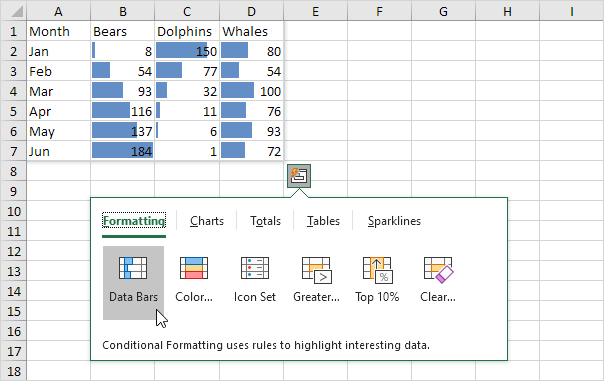
Formatting
Data bars, color scales and icon sets in Excel make it very easy to visualize values in a range of cells.
1. Select a range of cells and click the Quick Analysis button.
2. To quickly add data bars, click Data Bars.
Note: a longer bar represents a higher value. Visit our page about Data Bars to learn more about this topic.
3. To quickly add a color scale, click Color Scale.
Note: the shade of the color represents the value in the cell. Visit our page about Color Scales to learn more about this topic.
4. To quickly add an icon set, click Icon Set.
Note: each icon represents a range of values. Visit our page about Icon Sets to learn more about this topic.
5. To quickly highlight cells that are greater than a value, click Greater Than.
6. Enter the value 100 and select a formatting style.
7. Click OK.
Result. Excel highlights the cells that are greater than 100.
Note: visit our page about Conditional Formatting to learn much more about this topic.
Charts
You can use the Quick Analysis tool to quickly create a chart. The Recommended Charts feature analyzes your data and suggests useful charts.
1. Select a range of cells and click the Quick Analysis button.
2. For example, click Charts and click Clustered Column to create a clustered column chart.
Where Is Quick Analysis Tool In Excel On Mac Air
Note: click More to view more recommended charts. Visit our chapter about Charts to learn more about this topic.
Sparklines
Sparklines in Excel are graphs that fit in one cell. Sparklines are great for displaying trends.
1. Download the Excel file (right side of this page) and open the third sheet.
2. Select the range A1:F4 and click the Quick Analysis button.
3. For example, click Sparklines and click Line to insert sparklines.
Customized result:
Where Is Quick Analysis Tool In Excel On Mac
Note: visit our page about Sparklines to learn how to customize sparklines.